Finally I got some time to play with the new Azure Active Directory Sync tool and configuration. You can see the new features of this tool in Alex Simons’ blog - http://blogs.technet.com/b/ad/archive/2014/04/21/new-sync-capabilities-in-preview-password-write-back-new-aad-sync-and-multi-forest-support.aspx.
Installation
The installation was very straight forward. The step-by-step instruction are provided in the http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/azure/dn757602.aspx article. The administration tools and scripts are located in difference places which was little confusing in the beginning. There are three tools available to administer or customize the AAD sync configuration.
Synchronization Service Manager - C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\UIShell\miisclient.exe
Synchronization Rules Editor - C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\UIShell\SyncRulesEditor.exe
Synchronization Service Key Management - C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\Bin\miiskmu.exe
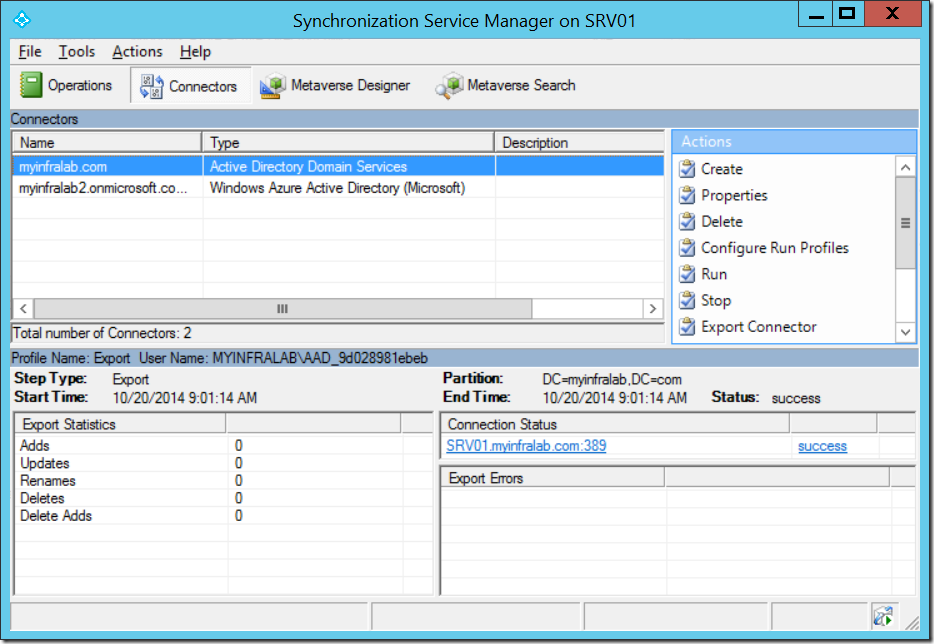
Synchronization Service Manager
This is where you administer or customize your synchronization options. It is an MIIS client. In the backend it creates Management Agent (MA) for your directory and Azure.
The default location of this file (missclient.exe) is in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\UIShell
Schedule
By default, the Azure AD sync schedule to run every 3 hours. It is Windows scheduled task as shown in the following screenshot:
You can manually force the replication from here if needed. In the backend it calls the DirectorySycnClientCmd.exe file which is located in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\Bin\ folder.
Note: If you have Office 365 in a hybrid mode, changing the default schedule or creating a custom schedule is not recommended or supported.
Object Filter and Customization
Object selection and customization can be performed using the Synchronization Service Manager tool.
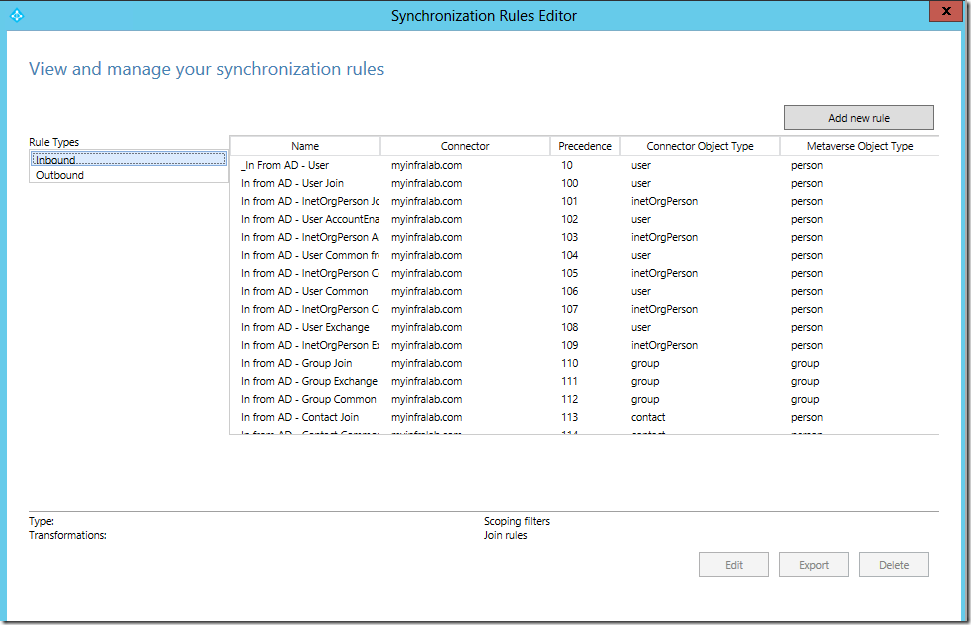
Synchronization Rules Editor
This is where you can create custom filters based on an attribute or attribute values. By default, this tool (SyncRulesEditor.exe) is located in C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\UIShell\folder.
You can create a new filter by selecting the Add new rule button in the Synchronization Rules Editor.
If you are planning to use an attribute based filer, make sure that the required attribute is selected (enabled) in the connector (MA) properties.

















1 comments:
How about geometry dash lite?
Post a Comment